Toshiba Unveils CMOS Millimetre Wave Circuit Simulation Model
Toshiba Corporation has developed a compact MOS-Varactor simulation model that delivers high level accuracy from DC to the millimetre wave (60 GHz) region.
The MOS (Metal oxide Semiconductor)-Varactor is a planar device, conventionally fabricated using CMOS technology. Generally, it is widely used in the frequency tuning block of the CMOS VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) circuits.
The new model was developed in cooperation with Professor Nobuyuki Itoh of Okayama Prefectural University.
The new compact MOS-Varactor model introduces an original algorithm to express scaling effects and can capture the impacts of parasitic effects that dominate in the 60 GHz region. Measurement parameters from 1MHz to 60 GHz for samples with different cell sizes were used for modelling. In general, it is difficult to express MOS-Varactor with a single model, but this newly developed model fully succeeds.
The new model's accurate capture of parasitic effects supports realisation of low power consumption in RF-CMOS products. Toshiba will use it a basic technology for developing such chips, key devices of the company's Analogue and Imaging IC Division. Building on the work done so far, Toshiba expects to secure accurate simulation of CMOS millimetre wave circuits in the future.
The new model has been verified with samples with cell lengths ranging from 0.26µm to 2.0µm formed with Toshiba's 65nm RF-CMOS technology. Very good accuracy for all cell sizes was achieved from DC to 67GHz.
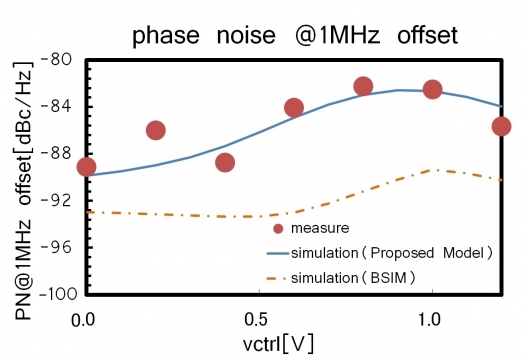
Verification of this model was made on a 60GHz circuit. Phase noise level dependency on the control voltage of the 60GHz VCO was measured and compared with a circuit simulation, with this model used in the frequency tuning block.
Measurement accuracy was found to be 8dB better than with the conventional model. The conventional model, the BSIM (Berkeley Short-channel IGFET Model) is generally utilised in simulating MOS-Varactor. It was developed by the University of California, Berkeley.
These development results were presented at APMC, the Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, held in Taiwan between December 4th and 7th.
































