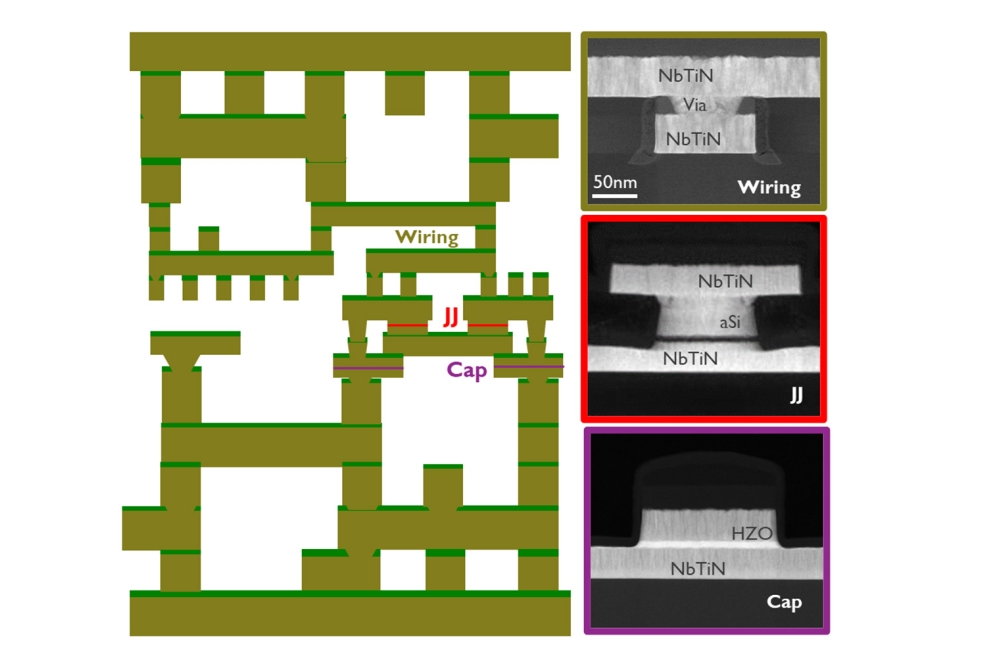
Researchers finds a way to reduce the overheating of semiconductor devices
Surface plasmon polariton breakthrough.
The demand to shrink the size of semiconductors coupled with the problem of the heat generated at the hot spots of the devices not being effectively dispersed has negatively affected the reliability and durability of modern devices. Existing thermal management technologies have not been up to the task. Thus, the discovery of a new way of dispersing heat by using surface waves generated on the thin metal films over the substrate is an important breakthrough.
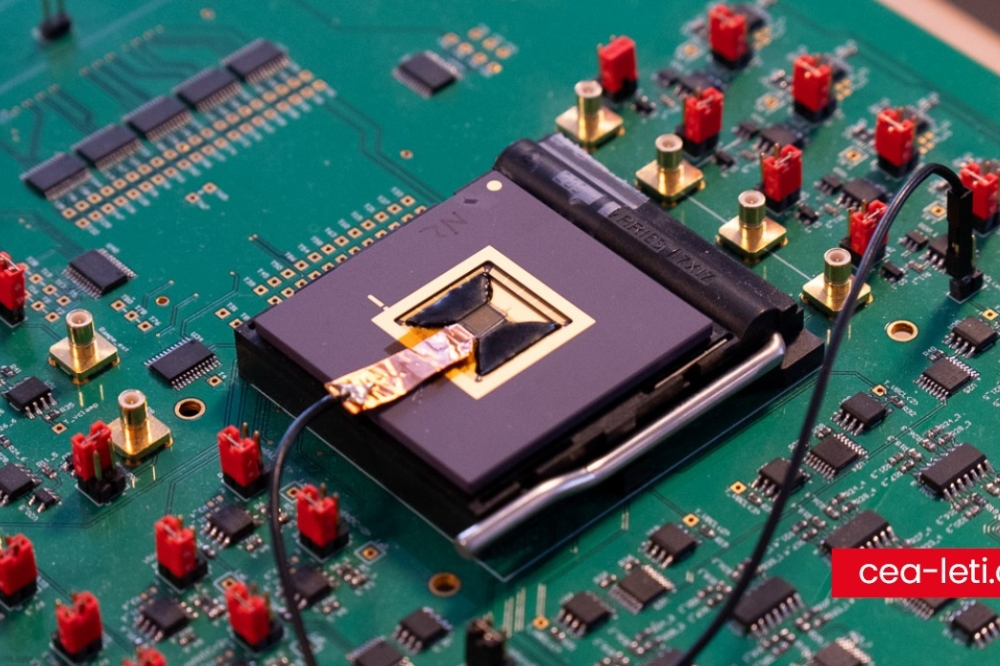
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that Professor Bong Jae Lee's research team in the Department of Mechanical Engineering succeeded in measuring a newly observed transference of heat induced by 'surface plasmon polariton' (SPP) in a thin metal film deposited on a substrate for the first time in the world.
Surface plasmon polariton (SPP) refers to a surface wave formed on the surface of a metal as a result of strong interaction between the electromagnetic field at the interface between the dielectric and the metal and the free electrons on the metal surface and similar collectively vibrating particles.
The research team utilized surface plasmon polaritons (SPP), which are surface waves generated at the metal-dielectric interface, to improve thermal diffusion in nanoscale thin metal films. Since this new heat transfer mode occurs when a thin film of metal is deposited on a substrate, it is highly usable in the device manufacturing process and has the advantage of being able to be manufactured over a large area. The research team showed that the thermal conductivity increased by about 25% due to surface waves generated over a 100-nm-thick titanium (Ti) film with a radius of about 3 cm.
KAIST Professor Bong Jae Lee, who led the research, said, "The significance of this research is that a new heat transfer mode using surface waves over a thin metal film deposited on a substrate with low processing difficulty was identified for the first time in the world. It can be applied as a nanoscale heat spreader to efficiently dissipate heat near the hot spots for easily overheatable semiconductor devices.”
The result has great implications for the development of high-performance semiconductor devices in the future in that it can be applied to rapidly dissipate heat on a nanoscale thin film. In particular, this new heat transfer mode identified by the research team is expected to solve the fundamental problem of thermal management in semiconductor devices as it enables even more effective heat transfer at nanoscale thickness while the thermal conductivity of the thin film usually decreases due to the boundary scattering effect.
This study was published online on April 26 in 'Physical Review Letters' and was selected as an Editors' Suggestion. The research was carried out with support from the Basic Research Laboratory Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.