Columbia engineers develop flexible lithium battery for wearable electronics
Shaped like a spine, new design enables remarkable flexibility, high energy density, and stable voltage no matter how it is flexed or twisted.
The rapid development of flexible and wearable electronics is giving rise to an exciting range of applications, from smart watches and flexible displays"”such as smart phones, tablets, and TV"”to smart fabrics, smart glass, transdermal patches, sensors, and more. With this rise, demand has increased for high-performance flexible batteries. Up to now, however, researchers have had difficulty obtaining both good flexibility and high energy density concurrently in lithium-ion batteries.
A team led by Yuan Yang, assistant professor of materials science and engineering in the department of applied physics and mathematics at Columbia Engineering, has developed a prototype that addresses this challenge: a Li-ion battery shaped like the human spine that allows remarkable flexibility, high energy density, and stable voltage no matter how it is flexed or twisted. The study is published today in Advanced Materials.
"The energy density of our prototype is one of the highest reported so far," says Yang. "We've developed a simple and scalable approach to fabricate a flexible spine-like lithium ion battery that has excellent electrochemical and mechanical properties. Our design is a very promising candidate as the firstgeneration, flexible, commercial lithium-ion battery. We are now optimizing the design and improving its performance."
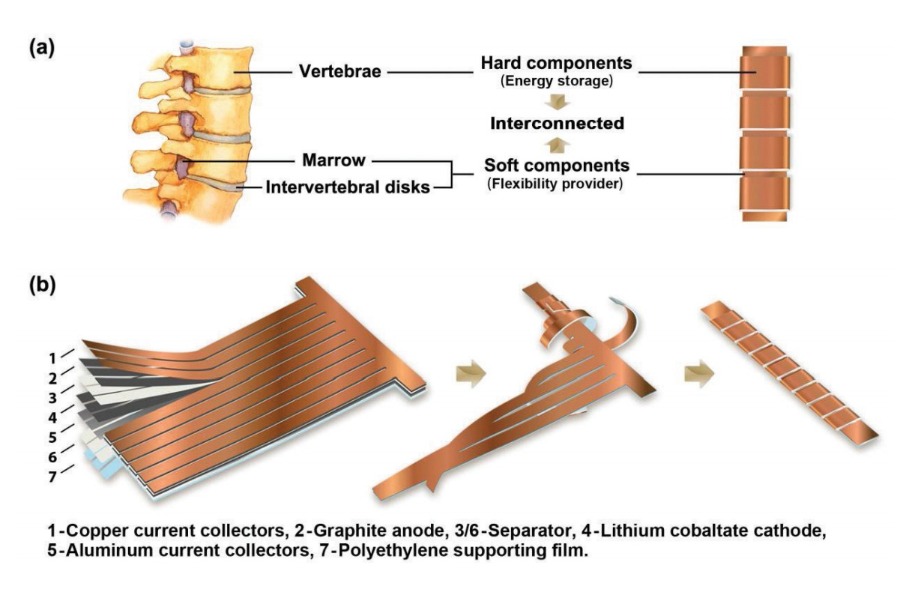
Yang, whose group explores the composition and structure of battery materials to realize high performance, was inspired by the suppleness of the spine while doing sit-ups in the gym. The human spine is highly flexible and distortable as well as mechanically robust, as it contains soft marrow components that interconnect hard vertebra parts.
Yang used the spine model to design a battery with a similar structure. His prototype has a thick, rigid segment that stores energy by winding the electrodes("vertebrae") around a thin, flexible part ("marrow") that connects the vertebra-like stacks of electrodes together. His design provides excellent flexibility for the whole battery.
"As the volume of the rigid electrode part is significantly larger than the flexible interconnection, the energy density of such a flexible battery can be greater than 85 percent of a battery in standard commercial packaging," Yang explains. "Because of the high proportion of the active materials in the whole structure, our spine-like battery shows very high energy density"”higher than any other reports we are aware of. The battery also successfully survived a harsh dynamic mechanical load test because of our rational bio-inspired design."
Yang's team cut the conventional anode/separator/cathode/separator stacks into long strips with multiple "branches" extending out 90 degrees from the "backbone." Then they wrapped each branch around the backbone to form thick stacks for storing energy, like vertebrae in a spine. With this integrated design, the battery's energy density is limited only by the longitudinal percentage of vertebra-like stacks compared to the whole length of the device, which can easily reach over 90 percent.
The battery shows stable capacity upon cycling, as well as a stable voltage profile no matter how it is flexed or twisted. After cycling, the team disassembled the battery to examine the morphology change of electrode materials. They found that the positive electrode was intact with no obvious cracking or peeling from the aluminum foil, confirming the mechanical stability of their design.
To further illustrate the flexibility of their design, the researchers continuously flexed or twisted the battery during discharge, finding that neither bending nor twisting interrupted the voltage curve. Even when the cell was continuously flexed and twisted during the whole discharge, the voltage profile remained. The battery in the flexed state was also cycled at higher current densities, and the capacity retention was quite high (84 percent at 3C, the charge in 1/3 of an hour). The battery also survived a continuous dynamic mechanical load test, rarely reported in earlier studies. "Our spine-like design is much more mechanically robust than are conventional designs," Yang says. "We anticipate that our bio-inspired, scalable method to fabricate flexible Li-ion batteries could greatly advance the commercialization of flexible devices."
About the Study; The study is titled "Bio-inspired, spine-like flexible rechargeable lithium-ion batteries with high energy density."
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.

































