Sensor can aid organ transplant rejection
New technology under development at the Ohio State University is paving the way for low-cost electronic devices that work in direct contact with living tissue inside the body. The first planned use of the technology is a sensor that will detect the very early stages of organ transplant rejection.
Paul Berger, professor of electrical and computer engineering and physics at Ohio State, explains that one barrier to the development of implantable sensors is that most existing electronics are based on silicon, and electrolytes in the body interfere with the electrical signals in silicon circuits. Other, more exotic semiconductors might work in the body, but they are more expensive and harder to manufacture.
"Silicon is relatively cheap"¦ it's non-toxic," Berger says. "The challenge is to bridge the gap between the affordable, silicon-based electronics we already know how to build, and the electrochemical systems of the human body."
Paul Berger
In a paper in the journal Electronics Letters, Berger and his colleagues describe a new, patent-pending coating that that they believe will bridge that gap.
In tests, silicon circuits that had been coated with the technology continued to function, even after 24 hours of immersion in a solution that mimicked typical body chemistry.
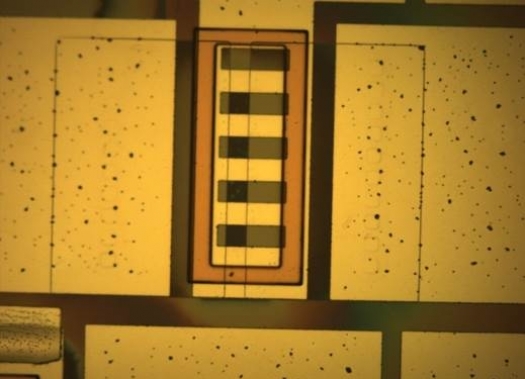
The photo at the top of this story shows a silicon circuit, coated with a protective layer and immersed in fluid that mimics human body chemistry. This photo is courtesy of Ohio State University.
The project began when Berger talked to researchers in Ohio State's Department of Biomedical Engineering, who wanted to build an insertable sensor to detect the presence of proteins that mark the first signs of organ rejection in the body. They were struggling to make a working protein sensor from gallium nitride.
"We already have sensors that would do a great job at detecting these proteins, but they're made out of silicon. So I wondered if we could come up with a coating that would protect silicon and allow it to function while it directly touched blood, bodily fluids or living tissue," explains Berger.
In the body, electrolytes such as sodium and potassium control nerves and muscles and maintain hydration. They do this by carrying a positive or negative electric charge that spurs important chemical reactions. But those same charges make the electrolytes attractive to silicon, which will readily absorb them. Once inside, the charges alter the electronic behavior of the silicon so that the readings of a sensor can't be trusted.
In the study, Berger's team tested whether electrolytes could be blocked from entering silicon with a layer of aluminium oxide.
The researchers submerged the coated test sensors in fluid for up to 24 hours, removed them from the solution, and then ran a voltage across them to see if they were working properly. The tests showed that the oxide coating effectively blocked electrolytes from the solution so the sensors remained fully functional.
Once developed, a device using this technology could detect certain proteins that the body produces when it's just beginning to reject a transplanted organ. Doctors would insert a needle into the patient's body near the site of the implanted organ. Silicon sensors on the needle would detect the protein, and doctors would know how to tailor the patient's dosage of anti-rejection drugs based on the sensor readings.
Berger believes this work is the first step towards fabricating devices that could be implanted in the body long-term.
Though the current study describes a silicon sensor coated with aluminium oxide, he envisions that other devices could utilise coatings made from other materials such as titanium. Such coatings could even be tailored to boost the performance of sensors or other biomedical devices.
In particular, Berger sees a potential use for coated polymer semiconductors that goes beyond sensing chemicals in the body. He suspects that such semiconductors could replace nerves in the body that have been damaged by disease or injury.
"We could replace a damaged nerve with an artificial neuron and restore functionality immediately, and that's a really exciting possibility," Berger says.
Berger's team is working with Ohio State researchers Tom Rosol, professor of veterinary biosciences, and Phillip Popovich, professor of neuroscience, to explore that possibility.
Coauthors on the Electronics Letters paper included former doctoral students Anisha Ramesh, Fang Ren, Patricia Casal and Samit Gupta; current doctoral student in biomedical engineering Andrew Theiss, and Stephen Lee, associate professor of biomedical engineering. The university intends to license this technology for further development.

































