Panasonic & imec develop tiny MEMS energy harvester
Composed of many silicon related compounds, this device is suited to automotive applications
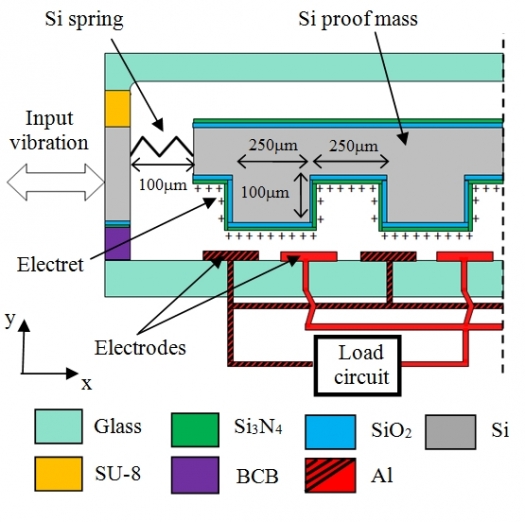
A team from imec and Panasonic have developed a new vibration energy harvester based on a corrugated SiO2-Si3N4 electret.
An electret is a dielectric material that has a quasi-permanent electric charge or dipole polarisation. An electret generates internal and external electric fields, and is the electrostatic equivalent of a permanent magnet.
This latest MEMS device has a footprint of only 1cm² and has been developed for tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS). It generates a maximum power of 160µW when excited by a sinusoidal vibration.
With noise vibrations such as in a tire, the generated power is between 10 and 50µW, which is enough to power a simple TPMS module.
This harvester was presented at the recent 17th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, based in Barcelona.
To improve road safety, TPMS have been made mandatory for all new cars in the US, with the EU to follow. For the comfort of the user and to limit the costs, TPMS need a compact and long-lasting power supply that doesn't need to be replaced during the lifetime of the tire.
Because there are abundant mechanical vibrations inside a tire, a potential solution is to use a vibration energy harvester. Such harvesters convert ambient mechanical energy into useable electrical energy.
They can be fabricated with MEMS fabrication technologies, allowing for low production costs and a high reliability.
The new harvester that imec has developed is an electrostatic harvester. It is fabricated by stacking three wafers and bonding them. The central wafer contains a mechanical resonator made of a proof mass and springs etched in silicon.
The proof mass carries a corrugated electret on its bottom side, obtained by Corona charging of a SiO2-Si3N4 stack. The bottom wafer is made of glass and includes two metallic electrodes that are connected to a load circuit. The top glass wafer is used as capping to protect the device and to allow vacuum encapsulation.
A schematic of the device is shown at the top of this story.
When the harvester is subjected to an external vibration, the proof mass moves relative to the package and eventually starts to resonate. As a result, the electric field generated by the permanent charges of the electret induces countercharges on both electrodes of the bottom wafer.
The amount of countercharges on each electrode is equal to the flux of the electric displacement across their surfaces. When the mass supporting the electret moves, the electric field along the gap changes and so do the countercharges induced on each electrode. This results in an electric current flowing through the load circuit connected between the two electrodes.

































