Nanotechnology aids in cooling electrons without external sources
A team of researchers has discovered a way to cool electrons to -228 °C without external means and at room temperature, an advancement that could enable electronic devices to function with very little energy.
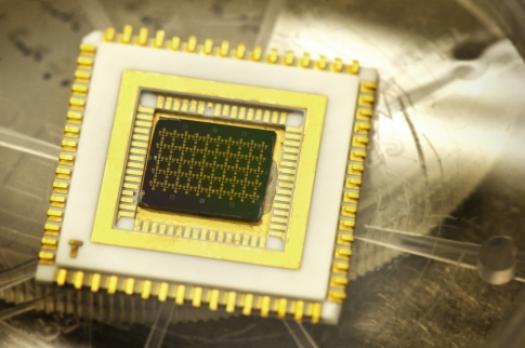
![]()
A chip, which contains nanoscale structures that enable electron cooling at room temperature,
The process involves passing electrons through a quantum well to cool them and keep them from heating.
The team details its research in "Energy-filtered cold electron transport at room temperature," which was published in Nature Communications.
"We are the first to effectively cool electrons at room temperature. Researchers have done electron cooling before, but only when the entire device is immersed into an extremely cold cooling bath," said Seong Jin Koh, an associate professor at UT Arlington in the Materials Science & Engineering Department, who has led the research. "Obtaining cold electrons at room temperature has enormous technical benefits. For example, the requirement of using liquid helium or liquid nitrogen for cooling electrons in various electron systems can be lifted."
Electrons are thermally excited even at room temperature, which is a natural phenomenon. If that electron excitation could be suppressed, then the temperature of those electrons could be effectively lowered without external cooling, Koh said.
The team used a nanoscale structure "“ which consists of a sequential array of a source electrode, a quantum well, a tunneling barrier, a quantum dot, another tunneling barrier, and a drain electrode "“ to suppress electron excitation and to make electrons cold.
Cold electrons promise a new type of transistor that can operate at extremely low-energy consumption. "Implementing our findings to fabricating energy-efficient transistors is currently under way," Koh added.
Khosrow Behbehani, dean of the UT Arlington College of Engineering, said this research is representative of the University's role in fostering innovations that benefit the society, such as creating energy-efficient green technologies for current and future generations.
"Dr. Koh and his research team are developing real-world solutions to a critical global challenge of utilizing the energy efficiently and developing energy-efficient electronic technology that will benefit us all every day," Behbehani said. "We applaud Dr. Koh for the results of this research and look forward to future innovations he will lead."
Usha Varshney, program director in the National Science Foundation's Directorate for Engineering, which funded the research, said the research findings could be vast.
"When implemented in transistors, these research findings could potentially reduce energy consumption of electronic devices by more than 10 times compared to the present technology," Varshney said. "Personal electronic devices such as smart phones, iPads, etc., can last much longer before recharging."
In addition to potential commercial applications, there are many military uses for the technology. Batteries weigh a lot, and less power consumption means reducing the battery weight of electronic equipment that soldiers are carrying, which will enhance their combat capability. Other potential military applications include electronics for remote sensors, unmanned aerial vehicles and high-capacity computing in remote operations.
Future research could include identifying key elements that will allow electrons to be cooled even further. The most important challenge of this future research is to keep the electron from gaining energy as it travels across device components. This would require research into how energy-gaining pathways could be effectively blocked.

































